Case study:
Henkel AG.
The creation and implementation of Henkel's global smart building standards.
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA aims to make its buildings smarter worldwide. The company deliberately goes beyond individual measures and isolated tools.
Instead, Henkel is pursuing a scalable and holistic approach aimed at establishing a global smart building strategy. This framework is designed to create company-wide standards and optimally leverage synergies. The primary focus is on generating genuine added value for both building users and operators.
SmartBuilding.One impressed with an approach that seamlessly combines construction and IT expertise. This combination made it possible to unite smart building strategy, architecture, data concept, and user focus into a functioning whole.
Today, together with Henkel's interdisciplinary project team, we are developing and implementing the global Henkel Smart Building Standard for various buildings, including a Digital Twin platform and companion app.

From concept to a working smart building.
The blueprint for Henkel's global smart building strategy.

01
Initial situation:
Think globally, start locally
In 2020, Henkel launched its Smart Building initiative. They were looking for a partner to develop global standards and put them into practice. Instead of submitting traditional forms, we at SmartBuilding.One focused on creativity and concrete solutions: An application video answered the tender questions in a visually clear and easily understandable way, showcasing innovation rather than formalism. During a digital design sprint week that we designed, an initial Smart Building use case (indoor navigation) was developed. The result was compelling, and SmartBuilding.One won the tender.
02
The task in the project:
Global standards for smart buildings
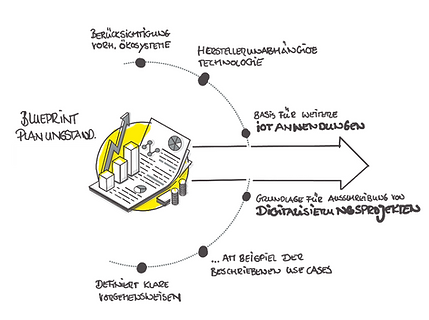
Henkel sought a scalable, sustainable solution for the digitalization of buildings. The goal of the process was to create a planning standard that describes manufacturer-independent technologies and solutions, taking the existing ecosystem into account. The resulting specifications were intended to form the basis for tenders for digitalization projects involving buildings and building technology. Digitalization is one of the megatrends of our time, and its associated applications play a central role in building management in the form of smart buildings. To realize a smart building with maximum security, energy efficiency, and enhanced comfort, building functions must be digitalized and networked, and processes automated. The automation of individual systems, such as air conditioning or heating controls, has long been an essential component in the construction and operation of buildings. What has changed in recent years, due to developments in areas such as the Internet of Things, cloud computing, and machine learning, is the pace of progress in networking all participants, innovations, and opportunities arising from digital possibilities. These should be captured and implemented in the form of a digitalization strategy for the operation of existing buildings as well as for the construction or revitalization of properties. The planning standard should serve as the basis for future planning of construction projects and modernizations.


03
The solution:
A holistic, interdisciplinary approach
Together, a solution was developed that integrates user needs, technology, and building design. The developed smart building planning standard is based on three core elements: human - building - technology. Communication and interaction between these elements are a crucial component of a future-oriented smart building strategy. Classifying the core topics creates a clear structure and allocation of the various themes and requirements for the planning standard. This method enables a clear structuring of use cases. The interplay of these three elements forms the basis for a sustainable smart building strategy.
04
The solution at a glance:
Scale step by step.
1) Development of globally standardized smart building standards. 2) User-centered definition and prioritization of use cases. 3) Integration into existing IT, IoT, and building systems. 4) Development of a scalable data and monitoring concept to increase efficiency. 5) Development of a holistic smart building strategy with internal teams. 6) Implementation and testing of use cases in real buildings. 7) Derivation of strategic recommendations for the implementation of use cases. 8) Ensuring intuitive, user-friendly operation of all applications. 9) Promotion of open, API-based, and vendor-independent IoT solutions. 10) Establishment of a standardized approach for integrating use cases. 11) Development of a scalable governance and administration structure at the client's site.

05
Key elements of the implementation:
This is how it was done
1) User-centered process with interviews, workshops, and co-creation. 2) Development of a Smart Building Ecosystem Map – the big picture for Henkel's future building and digitalization strategy. 3) Digital planning standard as a single source of truth. 4) Close stakeholder management and agile collaboration. 5) Custom-developed interfaces, prototypes, and a digital twin platform. The result is a scalable, modular system that can be adapted to new locations and use cases. It is based on the three core elements of the proposed solution.
06
The success:
From standards to measurable impact
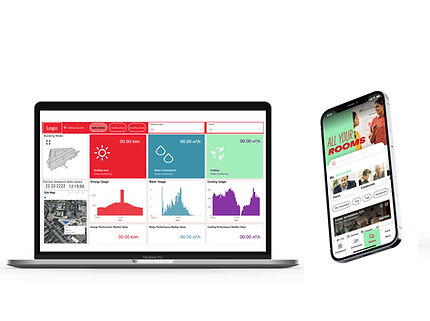
With this planning standard, Henkel now has a future-proof smart building strategy for its buildings – with clear standards, a technological foundation, improved efficiency, and real added value for Henkel employees: 1) Definition of the global smart building standard at Henkel. 2) Development of a global smart building strategy. 3) Support for projects and use cases at the Düsseldorf site. 4) Integration of the standards for global tenders. 5) Development of prototypes and MVPs. 6) Development of interfaces and integration into existing building and relevant company systems (APIs and interfaces, e.g., to SAP). 7) Digital Twin Platform: Data consolidation, monitoring of energy consumption and sustainability goals. 8) Companion App: Integration of room information, fault reporting, and integration options with other internal company applications.

Project information:
Industry: Adhesive Technologies / Consumer Brands
Building type: Laboratory and office space
Area: approx. 1.4 km² / approx. 230 buildings (Holthausen location)
Service phases: Consulting, planning & implementation
Duration: > 4.5 years (ongoing)
Key areas of focus: Strategy & project support, tender process, implementation, >20 use cases, development & integration of companion app & digital twin platform
Project data: 7 projects, +100 interviews, +3000 min. audio, 20 workshops (200 participants), approx. 500 Confluence pages
Participants: SmartBuilding.One, Carpus+Partner AG, Interactive Pioneers GmbH
Here's what our customers say.

